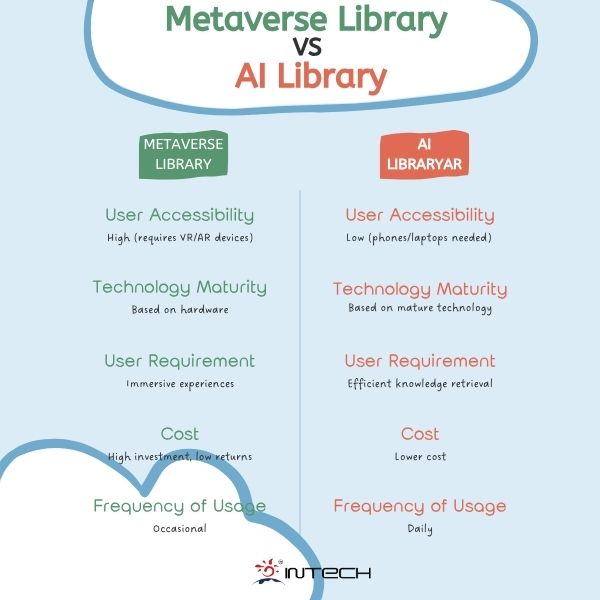
As the demand for knowledge sharing grows, emerging technologies are increasingly being integrated into library services, offering readers richer and more diverse learning resources. Among the most discussed trends are Metaverse Library and AI Library, which are often compared in terms of feasibility and real-world applications. Some even speculate "Will the future of libraries be completely dominated by the Metaverse?” Today, we explore the strengths and limitations of both technologies in the library landscape.
Metaverse Library
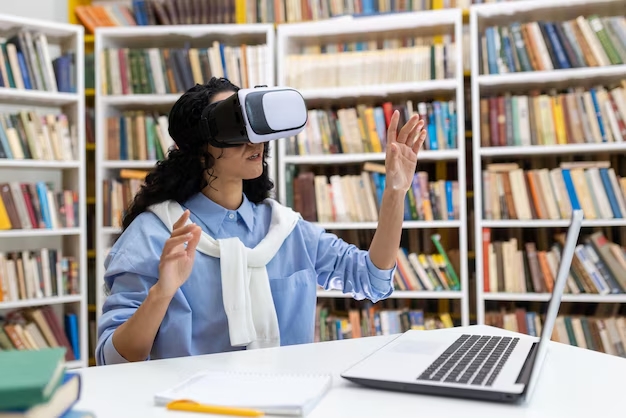
When the concept of Metaverse Library first emerged, many were captivated by its futuristic vision. Imagine putting on a VR headset and stepping into a digital library where you can flip through virtual books, interact with AI librarians, and explore immersive learning spaces. In this digital realm, libraries would no longer be just repositories of books, but fully interactive and experiential environments.
However, this vision remains largely idealistic rather than practical. Why?
1. Hardware Limitations
Not every user can afford VR headsets or high-end devices. For libraries, ensuring universal access to immersive experiences would require massive investments with uncertain long-term returns. The high entry barrier makes it difficult to justify widespread adoption.
2. Limited Functional Value
While virtual exploration may offer novelty, libraries exist to facilitate knowledge acquisition, not just entertainment. Users need efficient tools for research and learning—features that a purely virtual environment struggles to deliver effectively.
3. Isolation from Real-World Services
Metaverse libraries often operate as closed ecosystems, lacking seamless integration with traditional library functions like catalog search, interlibrary loans, or reference services. Without meaningful connections to real-world resources, their practical utility remains limited.
AI Library
Unlike Metaverse libraries, AI-driven libraries are already making tangible impacts. Advances in natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and big data analytics have transformed how libraries operate, offering smarter, more efficient services.
1. Enhanced Information Retrieval
AI-powered search engines can quickly locate relevant library materials without the help of library staff. Some systems even provide personalized recommendations based on user behavior.
2. Automation and Efficiency
AI streamlines library operations by automating cataloging, classification, and even answering frequently asked questions via chatbots. This allows librarians to focus on higher-level academic support rather than repetitive tasks.
3. Accessibility and Low Barriers
Unlike VR-dependent metaverse libraries, AI services are accessible through ordinary smartphones or computers, making them more inclusive and easier to adopt.
While the Metaverse library offers an exciting vision, its practical applications remain limited by cost, accessibility, and functional constraints. In contrast, AI libraries provide immediate and scalable benefits, enhancing research efficiency and accessibility.
In an era of information overload, libraries must prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and inclusivity—qualities that AI delivers far better than the Metaverse. The library of the future will not be a virtual playground but an AI-powered knowledge hub, revolutionizing how we learn and access information.
Previous:Gabrielle-Roy Library Named IFLA Public Library of the Year Award 2025
Next:Impact of Smart Lockers on Library Outreach and Engagement